

This individual would not be at risk for passing the disorder on to his/her offspring. There is a one in four (25%) chance the offspring will inherit no copies of the disease allele and will not express the phenotype or be a carrier. There is a one in two (50%) chance the offspring will inherit one copy of the disease allele and will be a carrier. There is a one in four (25%) chance the offspring will inherit two copies of the disease allele and will therefore have the phenotype. Typically, the parents of an affected individual are not affected but are gene carriers. In autosomal recessive inheritance, two copies of a disease allele are required for an individual to be susceptible to expressing the phenotype. Type O is routinely in short supply and in high demand by hospitals both because it is the most common blood type and because type O negative blood is the universal blood type needed for emergency transfusions and for immune deficient infants.
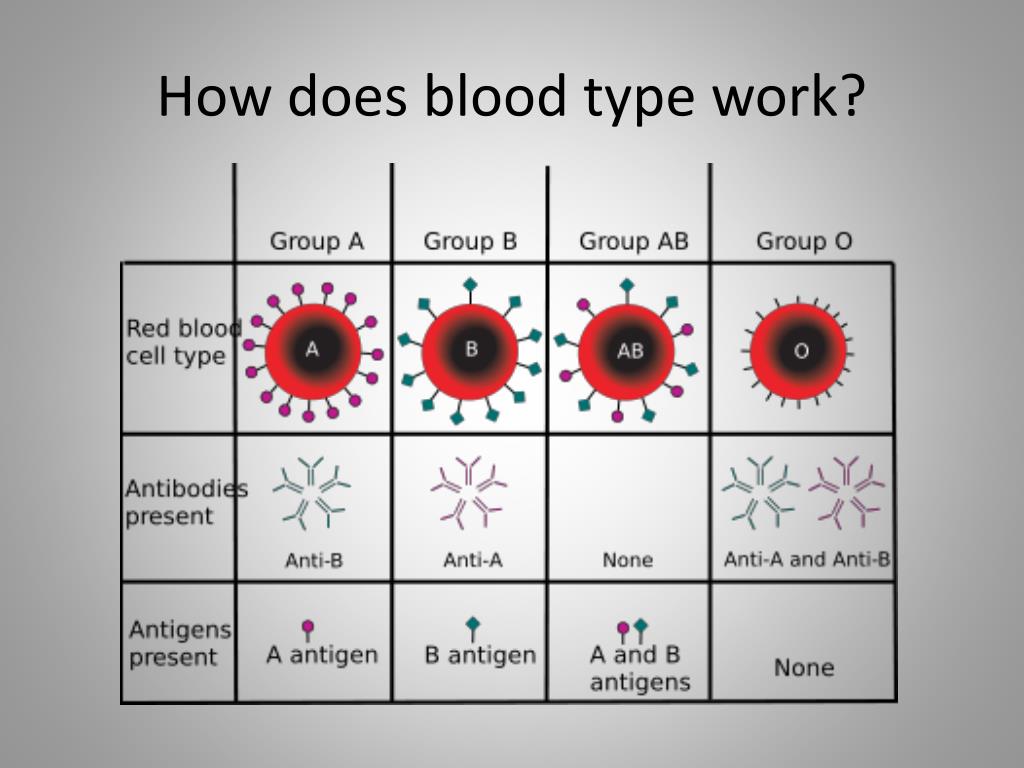
Why O negative blood can be used in transfusions for any blood type. The problem of the Rhesus factor can be when a Rhesus -negative woman gets a Rhesus. Male-to-male transmission can be observed.Įxamples of diseases with autosomal dominant inheritance include myotonic muscular dystrophy and Huntington disease. Universal donors are those with an O negative blood type. A blood type is a description of the individual composition of the. Unless a new mutation has occurred, all affected individuals will have at least one parent who carries the disease allele.Īutosomal dominant inheritance is often called vertical inheritance because of the transmission from parent to offspring.Īcross a population, the proportion of affected males should be equal to the proportion of affected females. With each pregnancy, there is a one in two (50%) chance the offspring will inherit the disease allele. In autosomal dominant inheritance, only one copy of a disease allele is necessary for an individual to be susceptible to expressing the phenotype.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
